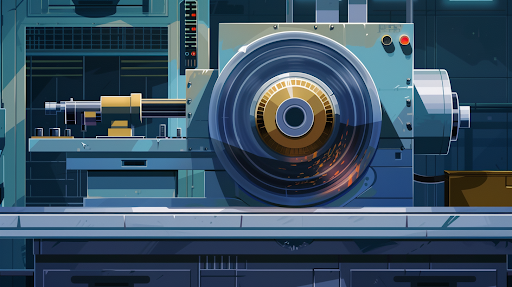
Grinding Wheels are important tools in various industries, from metal fabrication to woodworking. These abrasive powerhouses shape, sharpen, and smooth materials with precision. But it is true only when you use it in the right way. First of all, you must understand that a grinding wheel includes some basic specifications. These specifications include bond type, grain spacing, wheel grades, materials on which you can use it, and grain size.
The first thing you should consider while choosing a grinding wheel is the reason you will use it. Yet, selecting a wheel for the best performance and safety are the bond type, the grain’s attributes, the correct abrasive type, and the appropriate grit size. By now, you must be thinking about how you can read a grinding wheel’s specifications. Why delay anymore? Start reading this blog post now.
Basic Components of a Grinding Wheel Specification
A grinding wheel tells you the important parts that make up the wheel and how well it will work for different grinding jobs. So, here are the basic components of a grinding wheel specification.
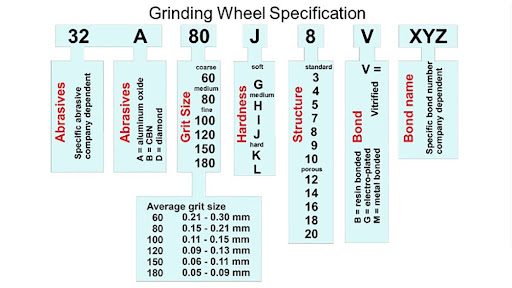
- Abrasive Type. It’s a useful abrasive that is made from aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, diamond, and CBN.
- Grit Size. The grit is the size of the abrasive particles in the sandpaper. Talking about sandpaper, large abrasive particles remove materials fast. But with finer grit, particles remove lesser materials.
- Grade. It refers to the bond’s strength that holds the abrasive grains together. Also, the difference between a hard and a soft grinding wheel is the bond structure. Softer bonds are important for more aggressive cuts than harder bonds.
- Structure. This is the spacing between the grains. Yet, the grains with higher density can affect the wheel’s cutting efficiency, coolant flow, and chip removal.
- Bond Type. The material that holds the abrasive grain together. Examples of this include vitrified, resin, metal, hybrid, and many more.
- Wheel Shape. It’s the geometric form of the wheel. As a result, it is tailored to specific grinding applications.
These parts work together to determine how well the grinding wheel performs. Moreover, it also decides what it can be used for. Hence, it makes sure that it gives the best results for each job.
Decoding the Specification Code on a Grinding Wheel
Decoding the specification code of a grinding wheel helps understand its composition and intended use. So, here are some standard markings that follow a specific format.
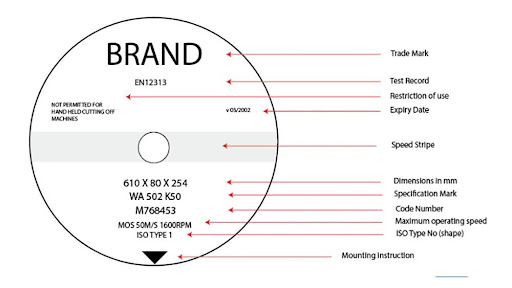
- Speed Stripe. It indicates the greatest safe operating speed, ensuring proper use and safety compliance.
- Dimension in Millimeters. This specifies its diameter, thickness, and bore size for accurate fitting and use.
- Specification Mark. It signifies the wheel’s grit size, hardness, bond type, and structure for appropriate application.
- Code Number. This identifies specific manufacturing details, batches, or models for traceability and quality control.
- Maximum Operating Speed. It indicates the highest safe rotational speed to prevent breakage and ensure safety.
6. Mounting Instruction. This provides guidelines for installing the wheel in the right way. Thus, it ensures safety and optimal performance.
Additional Codes of a Grinding Wheel
- Restriction of Use. It specifies prohibited use of the wheel to prevent improper use and user safety.
- Test Record. You can refer to this marking to check if the wheel is properly tested and fulfills the necessary safety standards.
- ISO Type. It reflects the dimensions and specifications of the wheel standardized by the “International Organization for Standardization” (ISO).
- Expire Date. This specifies the recommended date till which you can use the grinding wheel safely.
Understanding these components allows for the selection of the right grinding wheel for specific applications. Hence, it ensures efficiency and precision.
Abrasive Problem & Buy Grinding Wheel
Abrasive Types and Their Uses
Abrasive are materials used to polish surfaces through fiction. Moreover, they come in various types that suites for specific applications. So, here are some different abrasive types and how you can use them.

- Aluminum Oxide. It’s a versatile abrasive that is useful for grinding ferrous metals, stainless steel, and high-tensile alloys. Moreover, it also helps to remove sharp edges and burrs from metal parts. The materials used to make this abrasive are steel, aluminum, and non-ferrous metals. Apart from this, you can use it on stainless steel and tools steels. Moreover, it is helpful for some hard aluminum and bronze alloys.
- Silicon Carbide. It’s a hard and sharp abrasive tool that is ideal for cutting hard materials. Moreover, it is known for its high thermal conductivity and use in cast iron, ceramics, and composites.
- Diamond. This is super abrasive with extreme hardness. Diamond is useful for cutting, drilling, or grinding hard materials and shaping carbide, ceramics, and hard steels. This abrasive is also suitable for use on non-ferrous materials, such as ceramics and granite.
- CBN. This is an ideal abrasive used for grinding hard materials. Although this comes second to diamond in hardness, some basic parameters should be observed while selecting them. These common parameters are purity, toughness index, aspect ratio, morphology, and particle size distribution. They ensure CBN’s accuracy and wear-resistance strength.
In conclusion, choosing the appropriate abrasive type is important for achieving the desired finish and efficiency in various applications.
Steps for Grit Size Selection
Choosing the right grit size for abrasive ensures optimal surface finishing. Furthermore, it also helps with the efficiency of removing material from the surface you are working on.
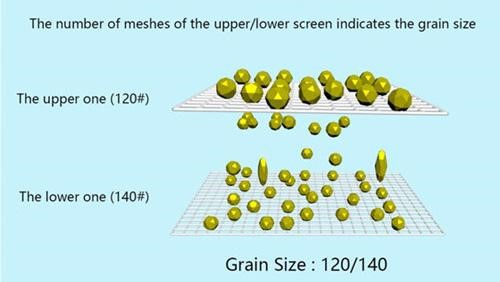
- Coarse Grits. It is ideal for quick material removal and rough grinding. Thus, it helps with rough shaping and leveling tasks while working on a metal or wood.
- Fine Grits. This is highly useful for achieving smooth and high-quality finishes. Also, it helps with the careful grinding of metals and hard materials requiring smooth finishes.
Selecting the right grit size carefully will help you to ensure effective and precise surface preparation and finishing.
Grade and Hardness of a Grinding Wheel
Grinding wheels come in various grades and hardness levels. Furthermore, each of them suits a specific task or material. So, here are some different grades and hardness levels of a grinding wheel.
- Soft Grades. You can use a soft-grade grinding wheel for low-pressure grinding or soft materials. The soft grade ranges from A to C.
- Hard Grades. These are useful for high-pressure grinding or hard materials. Also, Hard Grade wheels range from G to I.
Selecting the appropriate grade and hardness of a grinding wheel ensures efficient material removal and optimal surface finish.
Structure and Density of Grains in a Grinding Wheel
The structure and density of grains in a grinding wheel affect its performance and suitability for specific applications. So, go through the following structure and density of a grinding wheel.
- Open Structure. It is ideal for heat-sensitive materials and heavy stock removal. Moreover, you can also for efficient cooling and prevent workpiece overheating.
- Dense Structure. The benefits of using a sense grain structure are precision grinding and achieving fine finishes. Furthermore, it provides stability and accuracy in shaping and smoothing surfaces.
Understanding the structure and density of a grinding wheel helps in selecting the right wheel. Also, it helps in choosing the right wheel for achieving the balance between material removal, uneven heat, and surface finish.
Bond Types and Their Properties in a Grinding Wheel
The bond type of a grinding wheel determines its strength, hardness, and ability to keep abrasive grains. So, here are some different types of bonds and their properties in a grinding wheel.
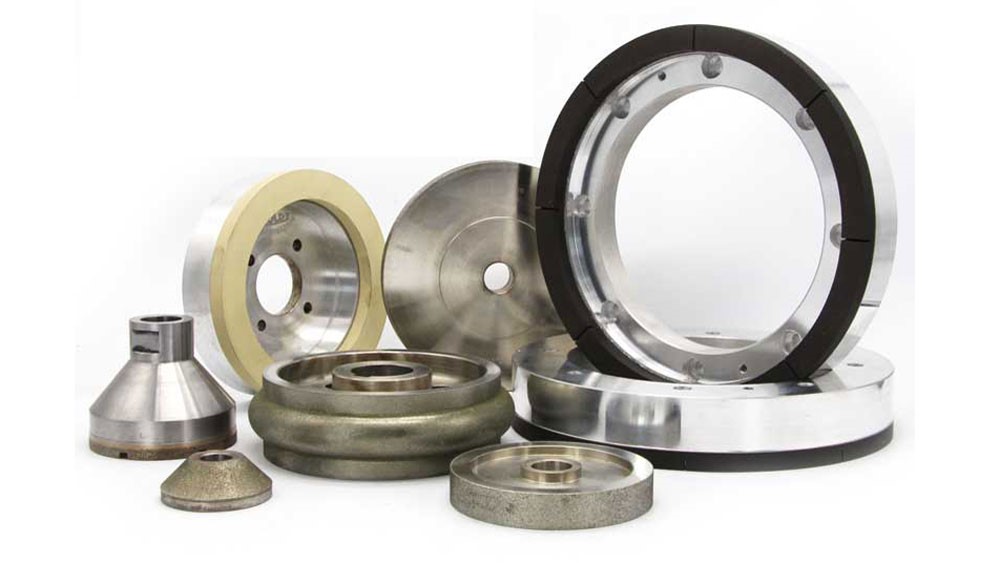

- Vitrified Bonds. It is known for its high rigidity and thermal stability. Also, it is suitable for precision grinding and high-temperature applications.
- Resinoid Bonds. This bond offers flexibility and impacts resistance at the same time. Besides, it is ideal for complex shapes and reduces vibrations during the grinding process.
- Metal Bonds. It provides durability and hardness. Thus, it is useful for grinding hard materials and achieving longer tool life.
- Hybrid Bonds. This bond combines properties from different bonds for specialized applications. Thus, it is customizable to meet specific performance requirements.
Selecting the appropriate bond type for a grinding wheel is important. This is because it impacts performance, surface finish quality, and wheel longevity.
Practical Examples of Reading Specifications about a Grinding Wheel
Reading specifications about a grinding wheel involves going through important details. Thus, it ensures that it meets the requirements of your applications. So, here are some practical examples of reading specifications about a grinding wheel.
Example 1: A60V.
- A. It’s the abrasive type (Aluminum Oxide in this case).
- 60. It’s the grit size (Larger Grit for heavy material removal).
- V. It’s the bond type (Vitrified and offers high rigidity and thermal stability).
A60V is suitable for general-purpose grinding where a high material rate is necessary.
Example 2: CBN200N100B.
- CBN. It’s an abrasive material (Cubic Boron Nitride).
- 200. It’s the grit size (fine grit for precision grinding).
- N100. It’s a concentration (medium concentration for abrasive particles).
- B. It’s a bond type (Resinoid provides flexibility and impact resistence).
Understanding these specifications ensures choosing a grinding wheel that optimizes performance, longevity, and safety for your grinding tasks.
Tips for Selecting the Right Grinding Wheel
Choosing the right grinding wheel is important for achieving efficient and effective grinding results across various uses. Go through the following section to learn about the tips that you should use to select the right grinding wheel.
Abrasive Problem & Buy Grinding Wheel
- Application Requirements. You should match the wheel specifications to the grinding tasks you want to carry out.
- Machine Compatibility. You should also ensure that grinding wheel dimensions are compatible with the machine’s spindle specifications.
- Operational Conditions. You should further check operational factors to prevent overheating and maintain workpiece integrity.
By following these tips, you can ensure the grinding wheel you select meets the requirements of your uses. As a result, it helps in achieving optimal performance and safety. With this saying, let’s bring this blog post to an end.
Concluding Everything
Abrasive wheels are important tools for shaping and smoothing materials in all industries. But their effectiveness depends on knowledge of their specifications. At the same time, key components determine the wheel’s performance and safety. Analyzing the specification code further ensures correct use and compliance with safety regulations.
Thus, choosing the right wheel helps in optimizing efficiency and precision. Yet, you can also match the wheel’s specifications as per your task requirements and maximize performance and safety. By following these guidelines, you can guarantee an efficient work process with improved safety measures.