Are you worried about the grinding wheel's scratching issues? It’s okay. We know that the immaculate finishing of the workpiece is not a walk in the park. Proper knowledge of every aspect involved is crucial for a presentable final product. Otherwise, certain scratching factors can secretly degrade and ruin your hard work in no time.
So, to protect you from this frustrating situation, this blog will discuss the most important factors influencing scratching on the grinding wheels in complete detail. So keep learning!
Figure No 1 Factors Influencing Scratching Of Grinding Wheels
Checklist
- What is scratching in grinding wheels?
- What are the factors influencing scratching in grinding wheels?
- Conclusion
1) What Is Scratching In Grinding Wheels?
“Scratching is the poor surface finishing of the workpiece due to uneven grating by the grinding wheels.”
What’s worse when you pass a product through several processes, and finally it comes out scratched? Scratching degrades the work piece's presentation and performance and affects its life span. Moreover, the unpleasing surface of the final article cuts its price in half, which is no doubt disturbing for operators and marketers.
Figure No 2 Scratching Of The Workpiece.
Although minor marks are ignorable, how can we ignore significant surface defects like deep ridges and gashes? Exactly! We can’t. Therefore, to solve the problem, we should first determine the root of the problem, such as what factors are contributing to the degrading of our valuable products. So, let’s delve into it!
2) What Are The Factors Influencing Scratching In Grinding Wheels?
Plenty of potential faults play a role in feed lines, spirals, and scratches on the workpiece, such as damaged tools, improper selection of wheels, high brittleness, and many more. Let’s converse about these elements one by one;
- i) Wheel loading
- ii) Irregular grit size
iii) Insufficient cooling fluid
- iv) Increment in friction coefficient
- v) Irregular grinding parameters
- vi) Faulty selection of grinding wheels
vii) Abrasive brittleness of grinding wheels
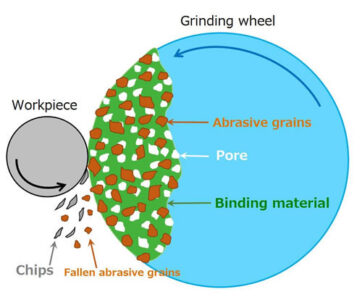
“After repeated grindings with the same wheel, some metal particles go deep down and start collecting in the pores of the wheel, ultimately creating heaviness and wheel loading.”
Wheel loading is one of the major aspects that causes scratching, imperfection, and a reduction in the overall performance of the grinding machine. Moreover, it not only devalues the workpiece but also reduces the lifespan and functioning ability of the grinding wheels.
Wheel loading is the result of some hidden sub-factors, such as improper hardness and softness of the grinding wheels, uneven wheel dressing, deficiency of coolant ( a liquid used to regulate temperature ), or incorrect grain size.
Ii) Irregular Grit Size
“Grit size is the actual size of the abrasive material particles on the grinding wheels.”
Grit size generally ranges from 12 grit ( 12 grains per inch) to 220 grit (220 grains per inch). If the grit size is larger, the grinding wheel particles will be finer, and your product will achieve maximum finishing. Likewise, if the grit size is lower, it will provide a fast but coarser finish.
Figure No 3 Abrasive Grains On Grading Wheel
As part of a grinding wheel, the improper size of abrasive particles directly affects the operational functionality of the grinding wheel. For example, if the particles are oversized, they may exert extra force on the workpiece, which could be the reason for deep scratches. In contrast, mini-size particles can cause wheel clogging.
Iii) Insufficient Cooling Fluid
“Cooling fluid is the liquid that helps regulate the temperature generated during grinding of the workpiece.”
If the coolant is insufficient, then the heat produced during the grinding process will remain stuck inside the system and soften the product, making it more prone to changes. Moreover, it will also soften the grinding wheel, which then could not provide the proper finishing to the workpiece, ultimately suspecting scars and scratching.
Iv) Increment In Friction Coefficient
V) Irregular Grinding Parameters
“Grinding parameters are the operational factors ( such as speed of the grinding wheel, feed rate, cutting rate, etc.) that regulate the processing of wheel grinding.”
If the speed of the grinding wheel is too fast or too slow ( improper with respect to the specific material ), it can cause tool marks and abrasions on the surface of the workpiece. You can check the wheel’s surface surface by applying short equations below:
Surface speed (SFPM) = ( π * Diameter (inch) * RPM )/12
Surface speed (m/s) = (π * Diameter (mm) * RPM )/60000
Another important parameter in determining the finishing level is the wheel's grinding pressure ( force per grain). If the contact area is larger, the force will be divided among all grain particles and less chance of grain fracture, so you can use a milder grade here. And if the area of contact is smaller, then each particle will experience severe pressure. Obviously, there will be more chance of shredding, so a harder grade is recommended in this situation.
If you overfeed or underfeed the grinding wheel ( more or less than its optimum capacity ), it will not be able to provide you with the desired finishing.
Vi) Faulty Selection Of Grinding Wheels
A compatible grinding wheel is a key factor in providing smoothness and flawless when finishing the final product. But if the grinding wheel’s size or its abrasion material doesn't suit the workpiece, it will certainly lead to an unprofessional and scratched product.
Figure No 4 Selection Of Grinding Wheels
One important thing to bear in mind is that the abrasive grains of the grinding wheel should be compatible with the material of the workpiece. For example; Aluminium oxide is best for ferrous metals, and silicon carbide can be used for non-metals and non-ferrous metal, etc.
Moreover, if the workpiece is easy to grind, use a harder grade because, during fast grinding, abrasive grains will shred more easily. So, using a harder grade ( strong bonds between wheel and grains ) will avoid fast grain breakage, which will expand the wheel’s life. And, if your material is hard to grind, just flip the recommendations.
Vii) Abrasive Brittleness Of Grinding Wheel
“Brittleness is the property of a material to break, crack or snap with some pressure.”
If the abrasive material is highly brittle and used to break and shred during the grinding process, the loose grain particles will get stuck between the wheel and workpiece, causing extra stress on the workpiece which creates feed lines and spirals on it.
Moreover, these shredded particles start collecting in the interspaces of the grinding wheel, ultimately contributing to wheel loading, which we have discussed above in the same section.
3) Conclusion