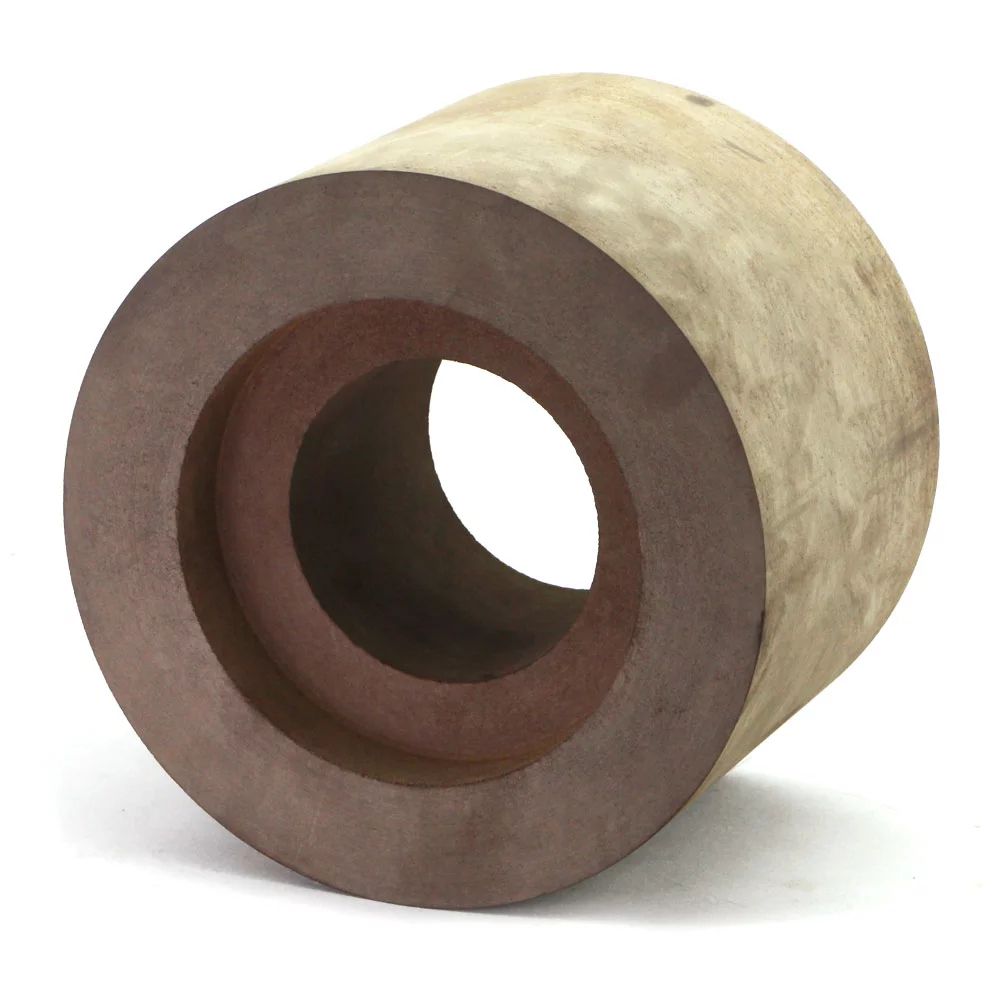
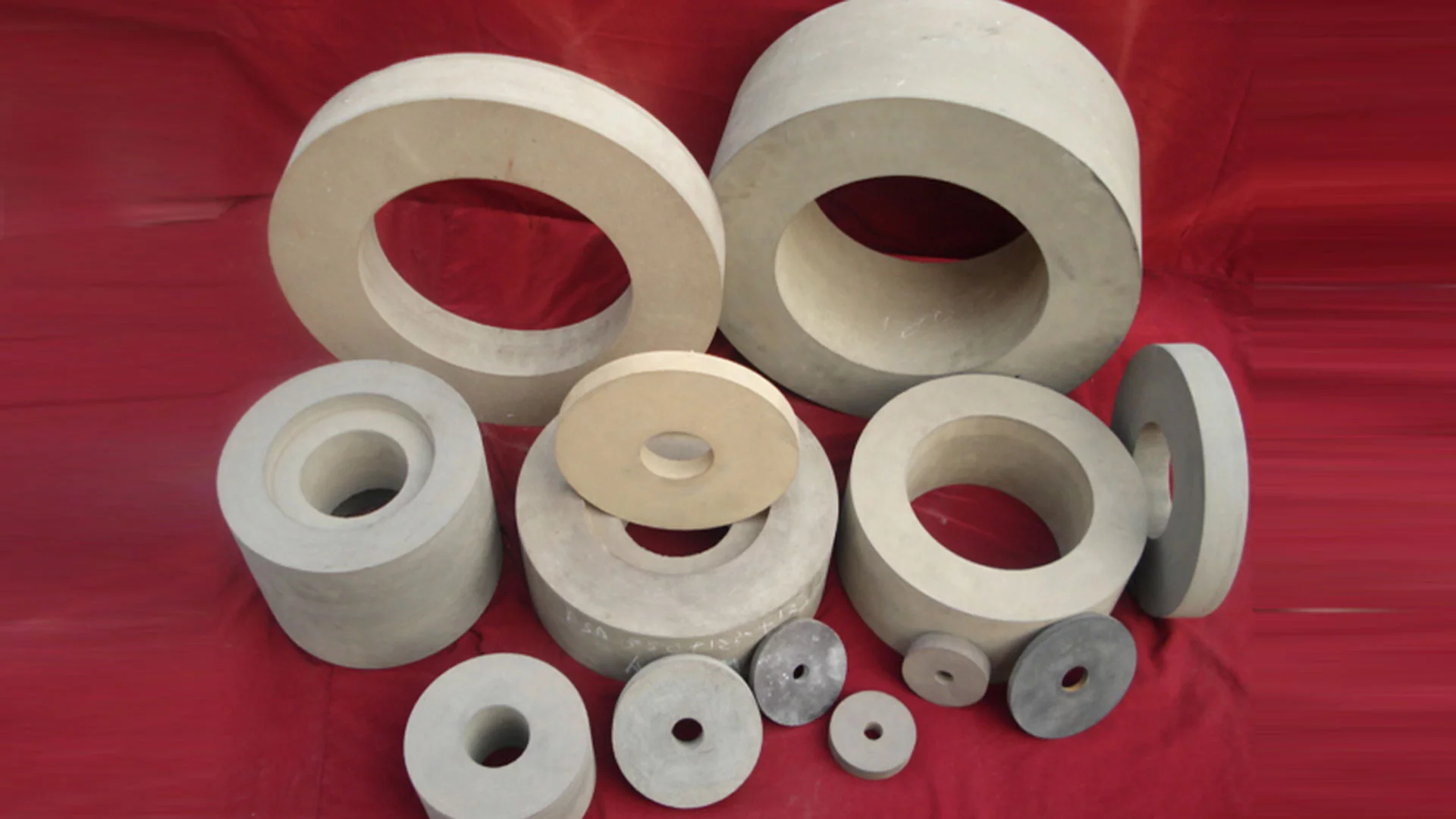
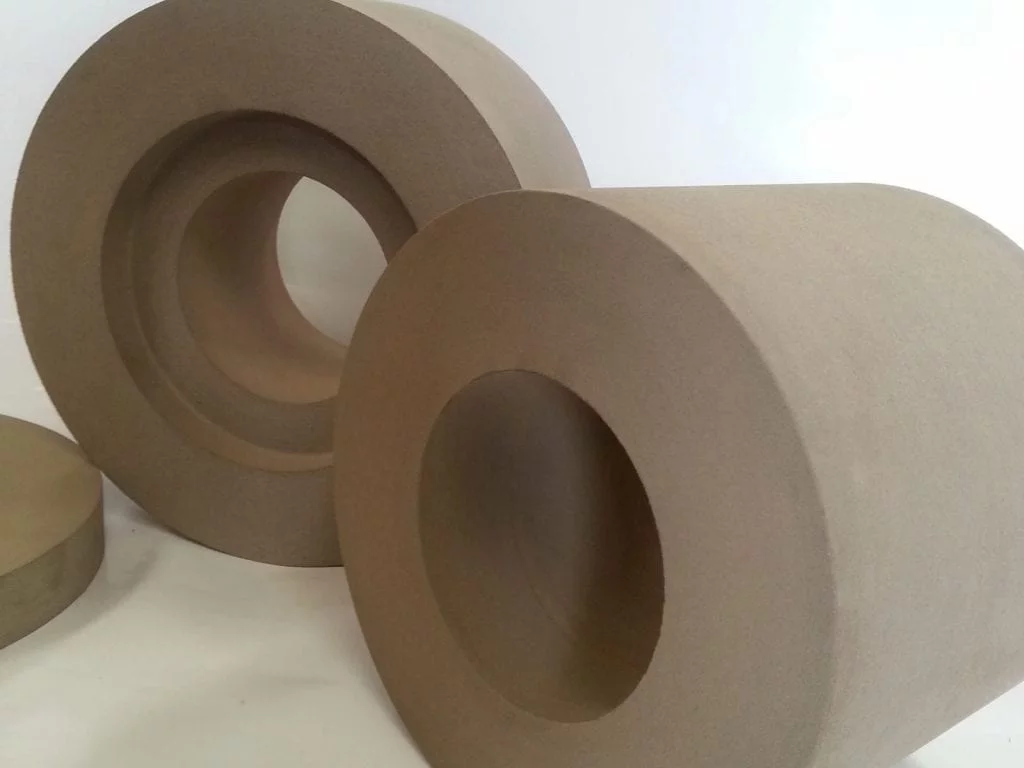
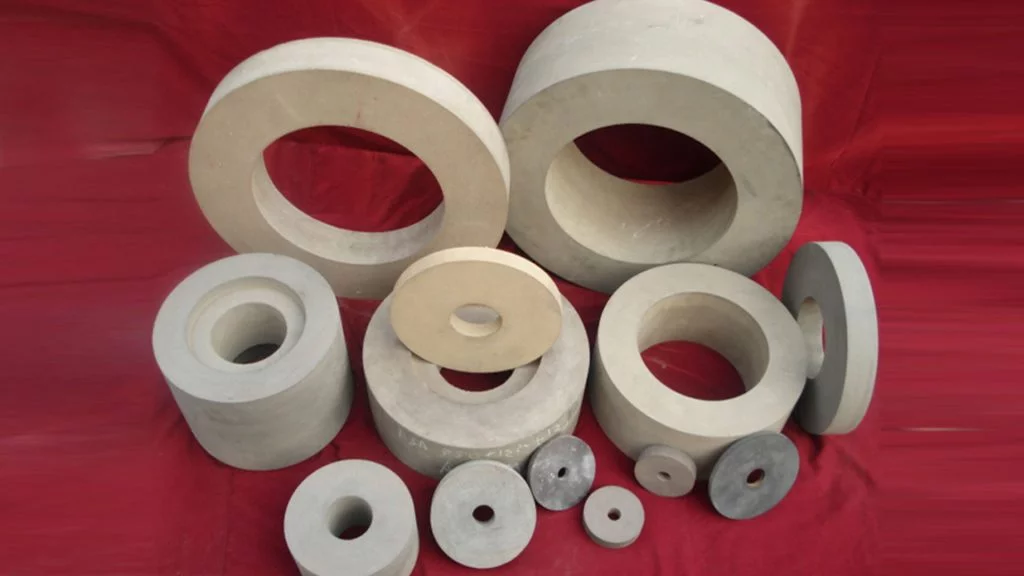
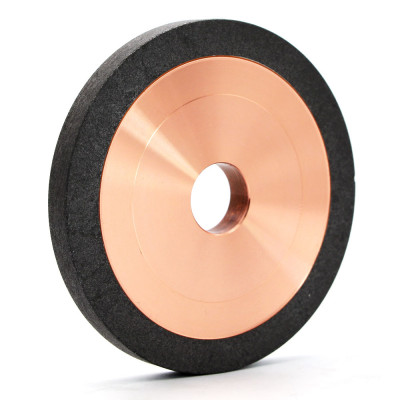
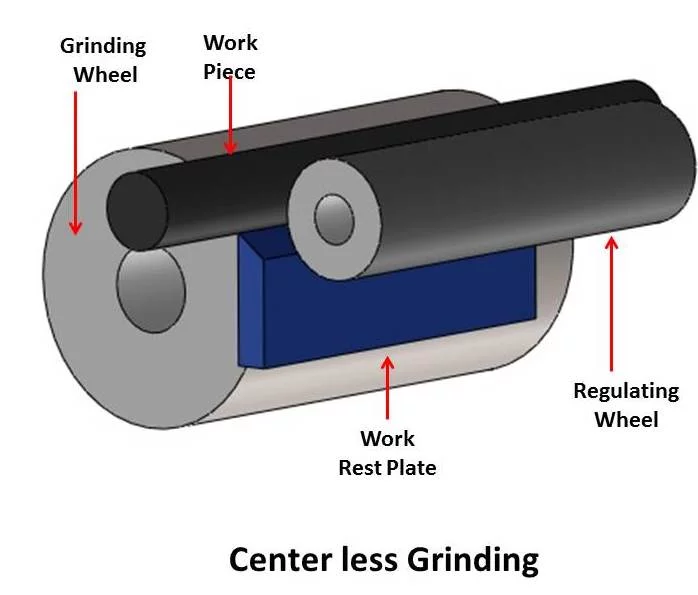
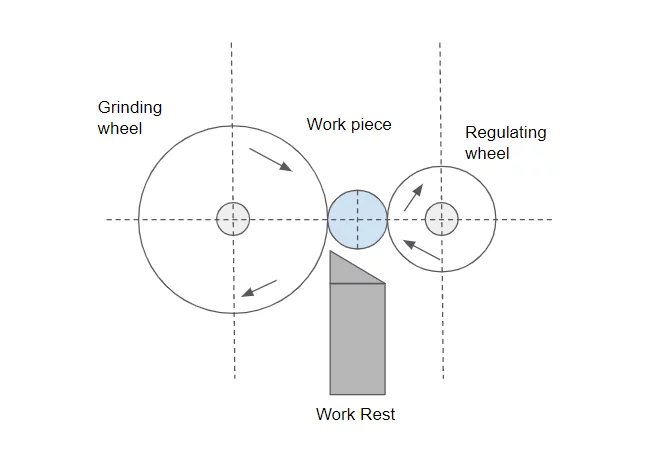
Brief Description of Rubber Regulating Wheel for Optimal Grinding:
The regulating wheel is made of abrasive rubber. Its job is to retain the workpiece against the grinding wheel, minimize pressure, and maintain the rotation under control. Rubber is a frequent component. Rubber regulating wheels are used as control wheels in centreless grinding. With diameters ranging from 50mm to 400mm and thicknesses varying from 25mm to 250mm, most wheels have straight and recessed edges. These regulating wheels are constructed with a 100 percent natural rubber bond matrix and are created to the most exacting standards. The matrix holds the abrasive grain in place, ensuring consistent abrasive exposure. These wheels have a good grip, so they can remove a lot of stock and rotate the workpiece steadily. Rubber Bonded Regulating Wheels (also known as Control or Feed Wheels) are produced utilizing a rubber calendaring method to provide the optimum results. Rubber regulating wheels are extensively used in a variety of sectors, including bearings, automobiles, hydraulics, and cutting tools.

- Wheel life is extended.
- Dressing frequency is reduced.
- Form retention is exceptional.
- A superior surface finish
- Enhanced efficiency
- Future-oriented
- With a solid link and less damage, you may expect a longer lifetime.
Detailed Description of Rubber Regulating Wheel:
-
Working Principle of Rubber Regulating Wheel in Centerless Grinding:
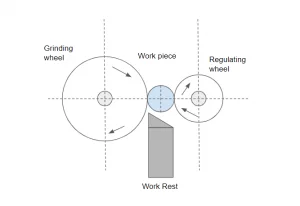
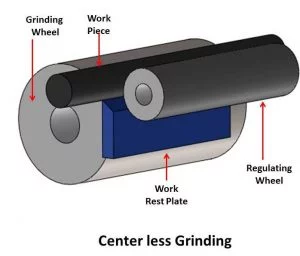
In centerless grinding, the workpiece is held between two wheels running in the same direction at different speeds and a workholding platform. One wheel, known as the grinding wheel, revolves on a fixed axis, directing the force exerted to the workpiece downward on the workholding platform. This wheel, which has a greater tangential speed than the workpiece at the point of contact, is usually used for grinding. On the other hand, the rubber regulating wheel is a moving wheel. This wheel is used to provide lateral pressure to the workpiece, and it usually contains an abrasive that is highly harsh or rubber-bonded to trap it.
(Working Principle)
The relative speed of the two wheels provides the grinding action, regulating the rate at which material is removed from the workpiece. Throughout the operation, the workpiece revolves with the rubber regulating wheel, with the same linear velocity at the point of contact and (ideally) no slippage. The grinding wheel increases its rotation and slides past the workpiece’s surface at the point of contact, removing material chips along the way.
-
Advantages of Rubber Regulating Wheels:
- continuous processing, no tool retractions, rapid clamping of the workpiece, and high productivity.
- The bracket and guide wheel placement mechanism is more durable than a standard cylindrical grinding machine’s top and center frame, and the stock removal is substantial, making it perfect for processing thin shaft workpieces. Using a rubber regulating wheel in conjunction with a centerless grinding wheel is also a simple way to accomplish high speed and powder grinding.
- A rubber regulating wheel is similar to a grinding wheel in that it is made of abrasive material, but it is usually combined with rubber or another similar material. As the name implies, a regulating wheel regulates the speed of a component as it revolves against a grinding wheel. A regulating wheel may be more crucial to the process than a grinding wheel since it controls the material removal rate, surface quality, and geometry.
-
Types of Centerless Grinding Processes Accompanied by Rubber Regulating Wheel:
The role of the regulating wheel, which is normally made of hard rubber and is abrasive, is to move the component being ground through the grinder through a Through-feed or In-feed operation. These processes rely on the rubber regulating wheel’s operation.
-
Role of Rubber Regulating Wheel in Through-feed Grinding:
The rubber regulating wheel’s inclination angle is normally between +1 and +3 degrees. This angle, together with wheel speed control, determines the part thru-feed rate in inches per minute (RPMs ranging from 15 to 300 RPM). The RPM speed is determined by the component’s size and length. If the RPM is set too high, chatter may develop. If the angle of the rubber regulating wheel is too acute, it might cause uneven wear, taper, and short wheel life. If the regulating wheel is too close to parallel with the grinding wheel, the pieces may stall between the wheels.
-
Role of Rubber Regulating Wheel in Infeed grinding:
Workpieces with intricate shapes are typically ground using infeed centerless grinding, which is similar to plunge grinding on a center-type machine. The workpiece rest blade must be tooled to match the part’s shape, and the grinding and rubber regulating wheels must be prepared to meet the part’s planned profile cut. The component is pushed against the grinding wheel by the rubber regulating wheel. The work does not move axially as it does in through-feed grinding. The Work Rest Blade’s Function in Supporting the Rubber Regulating Wheel:
Role of the Work Rest Blade in Supporting Rubber Regulating Wheel:
The purpose of the work rest blade is to maintain the component in touch with the rubber regulating wheel while it is machined. The centers of the regulating and grinding wheels are normally at the same height on a centerless machine, but the center of the workpiece rests higher on the work rest blade. The work rest blade’s height is important; for example, if the workpiece is put too high, it may clatter; if it is set too low, it may be out of round.
Role of Workpiece Angle in Centerless Grinding:
The top angle of the work rest blade is normally 30 degrees; however, it may range from 0 to 45 degrees. The angle is slanted in the direction of the portion’s driving regulating wheel. The angle of the workpiece rest blade is also important in centerless grinding. A thin wheel with a diameter of three to four inches may work well at 30 degrees, but a wider wheel with a diameter of six to ten inches may apply too much pressure to the grinding wheel, causing chatter, and may need a 20o to 25o angle. The rubber regulating wheel and Work Rest blade are important to the functioning of the Centerless Grinder, which is very adjustable equipment.
-
Manufacturing Process of Rubber Regulating Wheel:
One kind of organic bond wheel is the rubber regulating wheel. The basic raw material is either natural or synthetic rubber. When blended with abrasive grains like corundum or carbornudum, it has a greater bonding strength than resin. It may be used to bind extremely thin grinding wheels or cutting wheels with high flexibility. Because the pores in the rubber bonding agent polishing sheet are small, the voids are small, the structure is tight, and the form is effectively preserved, the concession property is excellent, especially at high temperatures. The rubber bond should be used within two years because of its poor heat, oil, and moisture resistance.
-
Installation of Rubber Regulating Wheel:
The rubber regulating wheel must be properly checked before being installed. It doesn’t matter whether it’s cracked or damaged. Before using, the test should be carried out following the standard. It is very banned to utilize it in any other way. Before installing the wheel, check the spindle speed on the machine tool and do not exceed the operating speed specified on the wheel. Only a certain nut wrench may be used to tighten the rubber regulating wheel, and it must be tightened in a symmetrical sequence on opposite sides of the main shaft. It must be a loose nut. It is not permitted to utilize a supplementary fixture or a tapping tool. Turn off the coolant to prevent the rubber regulating wheel from becoming imbalanced. The diameters of the rubber regulating wheel, grinding wheel spindle, and chuck must all meet the requirements. In the case of a protective cover, the newly installed grinding wheel must idle for at least 2 minutes at the working speed, and a grinding wheel with an outer diameter of 400 mm must idle for at least 5 minutes. When the grinding wheel is idle, the operator should not stand in front of it.
-
Notes For the Controlled Operation of Centerless Grinding Wheels:
- Before starting, examine the machine for damage and do not place anything on the machine table; instead, place the workpiece carefully.
- Before you begin, make sure the fuel tank’s oil level is normal, the cooling water tank’s water level is normal, the grinding wheel and the gap between the guide wheel and the supporting blade are normal, and the machine tool is clear of debris.
- Double-check the switches and ensure sure the safety measures, such as the protective cover, are operational before turning on the machine.
- Clean the centerless grinding wheels and the guide wheel dressing seat before starting, then fill the oil cup halfway with oil.
- Operators of the machine should be taught how to use it according to the operating instructions so that they may learn about different work ways.
- Check the oil system oil mirror and start the centerless grinding wheel and guiding wheel when the oil meter has stabilized
Summary:
The rubber regulating wheel is an organic bond wheel that aids in the appropriate grinding of the grinding wheel. It is beneficial in both cylindrical and centerless grinding operations. Rubber Bonded Regulating Wheels (also known as Control or Feed Wheels) are produced utilizing a rubber calendaring method to provide the optimum results. These wheels outperform the competition in terms of retention and efficiency. All instructions for using this wheel, including installation precautions and regulated operation, have been included. For best results, you should follow and read this tutorial.
More customized grinding wheels are available, contact us.