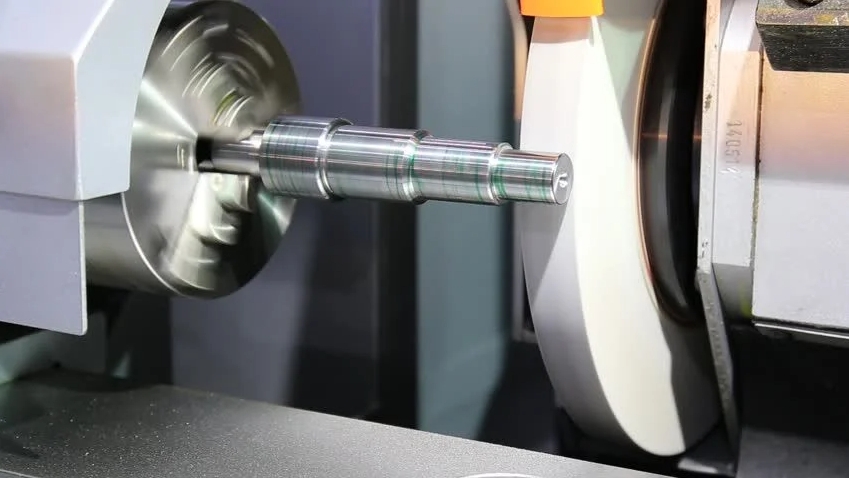
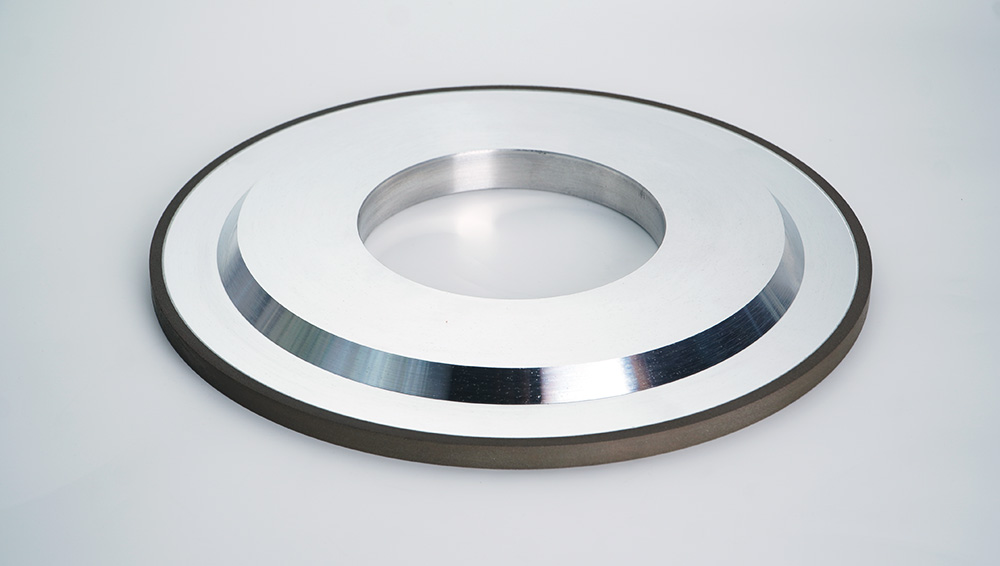
Grinding technology is a precision machining method that people use in metal processing. Moreover, it also involves fine processing of ceramics, glass, and other materials. For tougher materials, use softer wheels. This allows the used grains to fall off, revealing new sharp grains and keeping the wheel sharp. So, use harder wheels to use the grains before falling off. This prevents wasting the wheel and makes it last longer. For smoother surfaces, use finer grit wheels.
What is Grinding?
Grinding is a method of machining to use a wheel with rough particles to cut and shape materials. This process helps to make surfaces smooth and remove sharp edges. Moreover, it also helps in creating parts into the desired shape. You can perform grinding of various materials, such as metals, plastics, and ceramics. The process involves controlled contact between the grinding wheel and the material. The abrasive grains on the wheels remove tiny material chips. Thus, you can achieve the desired finish and precision.
Importance of Grinding in Different Industries
Grinding technology is an important aspect in various industries. This further helps with the precise shaping and finishing of materials. Go through this article to explore the importance of grinding in different industries.
- Manufacturing. The grinding process is important for creating smooth surfaces in the production of machinery parts.
- Automotive. The process also enables the precise shaping of engine components for maximum performance.
- Construction. This process also helps in preparing surfaces for constructing a building. As a result, it helps in ensuring structural integrity.
- Aerospace. Grinding also helps to ensure aerospace components meet strict safety and performance standards.
Grinding is important in all these industries for quality manufacturing. Thus, it further helps in shaping simple and complex products. Now, move on to the next section to learn about the diversity in grinding technology.
Abrasive Problem & Buy Grinding Wheel
Diversity of Grinding Processes
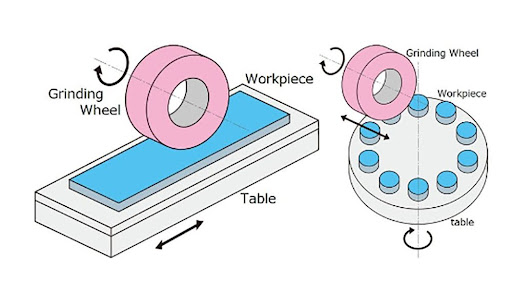
Grinding processes are many and varied. Besides regular external, internal, and surface grinding, there are specialized types. Examples include form grinding, tool grinding, and high-speed grinding. Each grinding method has its unique application scenarios and grinding requirements.
Now go through the following section and learn about different techniques. You can use these techniques for grinding processes.
External Cylindrical Grinding
In external cylindrical grinding, the hardness and the wheel grit size are important. This is because they influence how well the grinding process works. For tough materials, use softer wheels. This way, the worn-out grains can fall off, revealing new, sharp grains, and keeping the wheel sharp. So, use harder wheels so that the abrasive grains before they fall off. This prevents wasting the wheel and makes it last longer. For smoother surfaces, use wheels with finer grit. Maintaining stable grinding pressure and speed is also crucial to ensuring grinding quality.
Internal Cylindrical Grinding
Internal cylindrical grinding requires higher demands for wheel selection and usage techniques. The core reason is the limited operating space. People should choose wheels with good wear resistance and high thermal stability. Thus, it helps to ensure stable grinding effects in confined spaces. Controlling grinding depth and feed rate to avoid workpiece deformation or wheel damage is also crucial.
Surface Grinding
In surface grinding, the smooth operation of the wheel is crucial. It helps achieve high-quality flat surfaces. Thus, you should use well-balanced wheels, and check their balance state regularly. Choose the right wheel grit and hardness based on how flat & smooth the surface should be. Maintaining uniform grinding pressure and speed helps achieve the desired surface effect.
Form Grinding
Form grinding is useful for processing workpieces with complex shapes. In this process, the wheel’s shape and accuracy are important. This is because it determines the quality of the finished workpiece. Thus, high-precision, wear-resistant wheels should be useful. Also, the wheel shape should be according to the workpiece shape. Controlling grinding depth and feed rate ensures the accuracy and precision of the workpiece shape.
Tool Grinding
Tool grinding is useful in manufacturing and repairing tools. Examples include cutting tools and molds. Since these tools need high precision and wear resistance, high-quality, and high-precision wheels. During the grinding process, grinding parameters must be under control. Thus, it helps to ensure the sharpness and precision of the tools meet usage requirements.
High-Speed Grinding
High-speed grinding is useful in modern machining. Also, it helps to maintain high efficiency and high precision. The choice of wheels in this process is crucial. Moreover, it requires wheels with high thermal stability, and high wear resistance & strength. Thus, it helps to cope with the challenges of high-speed rotation & high-temperature environments. Additionally, grinding parameters must be in control. This further helps to prevent rapid wheel wear and workpiece overheating. The application of high-speed grinding technology improves machining efficiency. Also, it injects new vitality into modern manufacturing.
Real-Life Applications of Grinding Technology
Grinding is an important process in manufacturing and shaping components across various industries. Go through the following section to learn about real-life applications of grinding technology.
- Stampings. Grinding technology is useful to refine the edges & surfaces of stamped metal parts. Thus, it ensures uniformity and smoothness for assembly or further processing.
- Shafts. This technology is important for shafts for precise diameters, roundness, and surface finishing. Thus, it is important for rotational accuracy and reduced friction to mechanical assemblies.
- Bushings. It undergoes the grinding process for strict design parameters in inner & outer diameters. Bushings further ensure proper fit and function in assemblies requiring minimal clearance.
Carrying out the grinding process helps to achieve dimensional accuracy. Not only this, it also helps with surface quality and functionality integrity. It is true from simple stamping to complex machine parts and precision molds.
Future Trends of Grinding Technology
In the future, new grinding technology will make manufacturing efficient and eco-friendly. So, read this article and you will understand the future trends of grinding in no time.
- Advanced Materials. Grinding techniques will evolve to handle new materials. Examples of these materials include composites, ceramics, and advanced alloys. Moreover, they need specialized abrasives and methods for precise results.
- Industry 4.0 Integration. Automation and digitalization will drive grinding processes toward greater integration with smart factories. Furthermore, it will use AI and ML for real-life monitoring and adaptive control.
- Environmental Sustainability. There will be a push towards eco-friendly grinding technologies. They will include dry machining techniques, coolant alternatives, and recycling systems. Thus, they help to minimize waste and environmental impact.
These trends reflect a shift towards integrated, efficient, and sustainable grinding technologies. Moreover, they are driven by advancements in materials science in the manufacturing sector. Not only this, but even digitalization and environmental consciousness aid the manufacturing sector.
Summary of Wheel Usage Techniques
Grinding technology is a precision machining method important for shaping metals, and ceramics. It employs abrasive wheels to smooth surfaces and refine edges. As a result, it ensures precision in a lot of industries. From manufacturing to aerospace, grinding enhances product quality and performance. It happens by creating smooth finishes and precise shapes. Future trends include advancements in material handling and eco-friendly practices like dry machining. These innovations promise more efficient and sustainable manufacturing processes ahead.